
|
|
ACCESS CONTROL LISTS• Access Control Lists ACL • ACL Example • ACL Directory Example Access Control Lists ACL
ACL ExampleUser raspberry creates a directory (i.e. this directory is owned by raspberry and group is raspberry): Now, create a file called Testfile1.txt touch Testfile1.txt  Allow user fred to read and write to a file inside this directory called Testfile.txt setfacl -m u:fred:rw Testfile1.txt 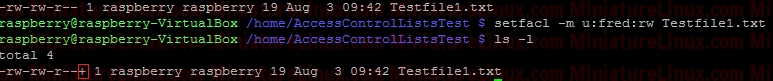 User fred can now edit this file (e.g. nano Testfile1.txt) and write to it etc… If I login as say another user like “jon”, then “jon” can’t edit this file because it is in a directory owned by raspberry and group raspberry with file permissions for Other of r-- so jon can read the contents of the file Testfile.txt but NOT edit it. To view the ACL properties of this Testfile.txt type the following: getfacl Testfile1.txt 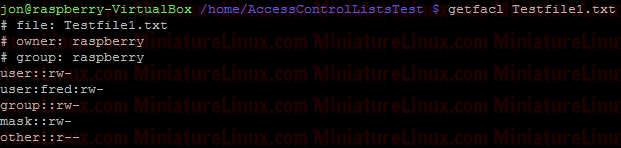 To remove the ACL completely: sudo setfacl -b Testfile1.txt  ACL Directory ExampleIf only the Users fred and gretchen (development group members) are allowed access to a directory and I’ve set up the directory so that any new files fred or gretchen create within this directory get the group name developer via the sticky bit:sudo chmod 2770 AccessControlListsTest Note that if I wanted to make sure that only Gretchen can delete her files in here that she creates and only fred can delete his files that he has created I would do the following as otherwise (in the above case) fred or grechen can delete each others files: sudo chmod 3770 AccessControlListsTest Anyway, I digress, I use: sudo chmod 2770 AccessControlListsTest The resulting Terminal output looks like:  Now I log in as fred and create a file fred.txt sudo fred touch AccessControlListsTest/fred.txt Now I log in as gretchen and create a file gretchen.txt sudo gretchen touch AccessControlListsTest/ gretchen.txt Now I log in as jon (who isn’t a member of group developer) and try and create a file jon.txt sudo jon =>Don’t have permission to create a file here:  However I don’t want jon to be a member of group developer but I do want him to be able to do whatever he likes inside this directory therefore, as user raspberry: setfacl -m u:jon:rwx AccessControlListsTest/ ls -l => We get the little “+” symbol signifying that ACL apply to this directory: 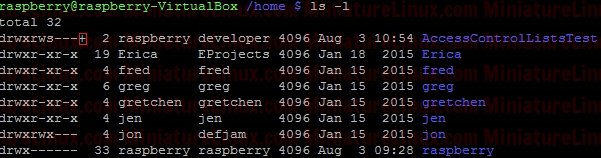 In order to see which ACL rules apply to this directory: getfacl AccessControlListsTest/ 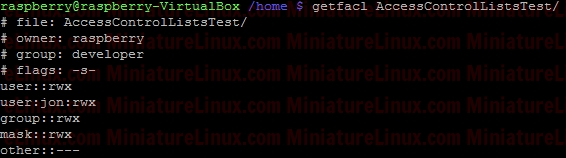 Now, as user jon can create a file in this directory as jon has read/write/execute permissions via Access Control Lists ACL: touch AccessControlListsTest/ jon.txt 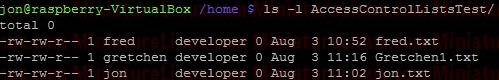 Note above that due to the sticky bit, the group of the file that jon created (jon.txt) has the group name developer even though jon isn’t a member of this group.  If I want to force user Others to have - - - permissions for any file they create within a directory called Testy: mkdir Testy chmod 777 Testy 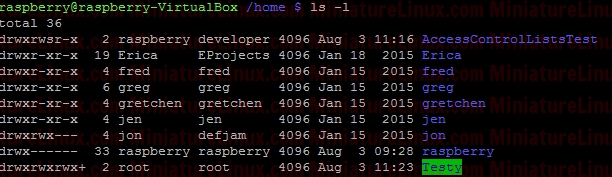 So, at the moment, this directory is setup so that everybody can wrx however it is owned by user root and group is root. For example, if user fred creates a file inside this Testy directory: su fred touch Testy/fred4.txt  As we can see above, the owner of this file is fred and the group of this file is fred. User other had read access (r - -) If I want to force the user Other to have - - - permissions for any files he create inside this directory i.e. For User “Others” to have permissions - - - despite the directory having permissions rwx rwx rwx sudo setfacl -m d:o:- Testy/ For directories, you can set ACL rights that will be assigned by defaults to files and directories created inside it. To do so, use the default identificator or the -d parameter. However, the default permissions will not be applied to the first directory. If user fred creates a file inside this dir now: 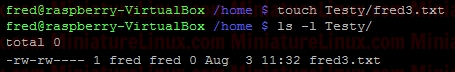 The file created has permissions for other as: - - - Note, to remove the ACL settings from this Test directory simply type: sudo setfacl -b Testy/ 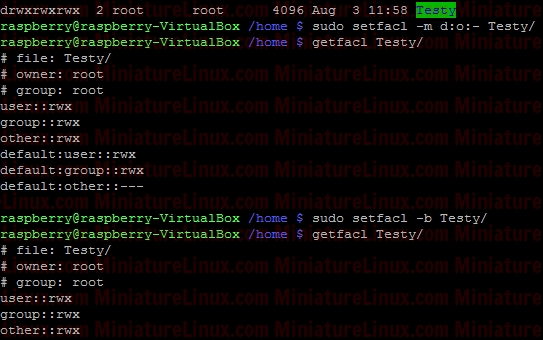 |
|
Linux Examples - Comments |
||